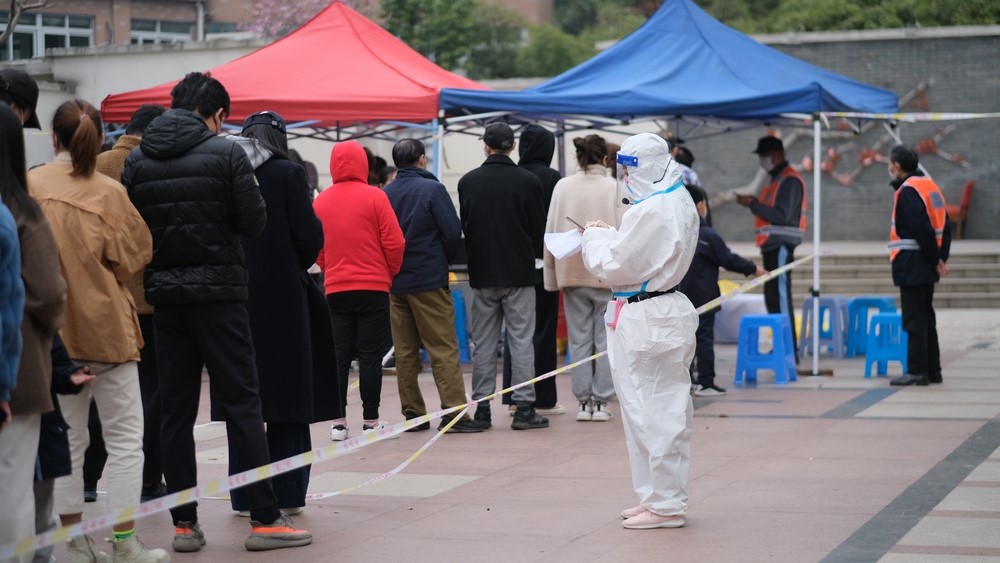
The virus is rarely fatal.
Others are reading now
The virus is rarely fatal.
What Is Chikungunya and Where Did It Come From?

Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne virus first identified in Tanzania in the 1950s.
Its name comes from a local word meaning “that which bends up,” referring to the bent posture caused by painful joints.
While rarely fatal, the virus causes long-lasting discomfort and is spreading in tropical and subtropical regions.
Key Symptoms: More Than Just a Fever

The virus often causes fever, headache, muscle pain, rash, and extreme fatigue.
Also read
But its most telling symptom is severe joint pain, which can last for weeks or even months.
In some cases, the pain is so intense that it limits movement and daily activities. Children and older adults may be more severely affected.
How the Virus Spreads: Not Person to Person
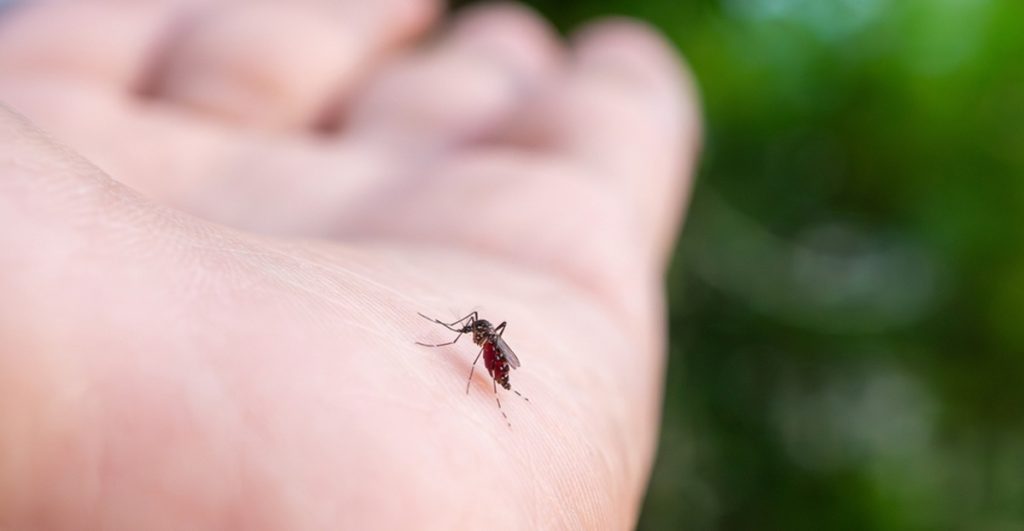

Chikungunya is not contagious between people.
It spreads only through the bite of an infected mosquito.
However, a person with the virus can pass it to a mosquito that bites them.
Also read
That mosquito can then infect others, allowing the virus to spread rapidly in mosquito-heavy areas.
Where Is It Found and Who’s at Risk?

Chikungunya is most common in parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
Recent outbreaks have occurred in India, Brazil, the Philippines, and now southern China.
Travellers to affected areas are at risk, especially those who don’t take proper mosquito precautions.
How to Protect Yourself from Infection
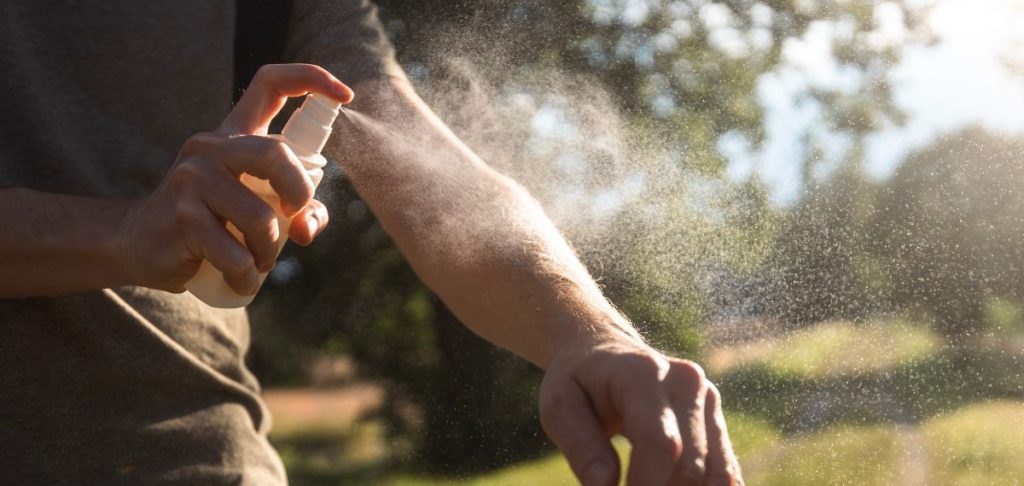

There is no cure for chikungunya, so prevention is key.
Also read
Use insect repellent, wear long-sleeved clothing, and sleep under mosquito nets in high-risk areas.
Emptying standing water around homes is one of the most effective ways to stop mosquito breeding.
Can You Get Vaccinated?
Yes, but only in limited cases.
Two vaccines (IXCHIQ and VIMKUNYA) have been approved in the US.
They are recommended for people travelling to outbreak zones.
Also read
The CDC currently advises vaccination for travel to parts of Asia and South America, including the Chinese city of Foshan.
Why Chikungunya Is Hard to Track

Because many of its symptoms are similar to dengue or Zika, chikungunya can be misdiagnosed, especially if joint pain is mild or absent.
This makes it difficult for health officials to know exactly how many people have the virus, or how far it has spread.
What to Do If You Get Sick
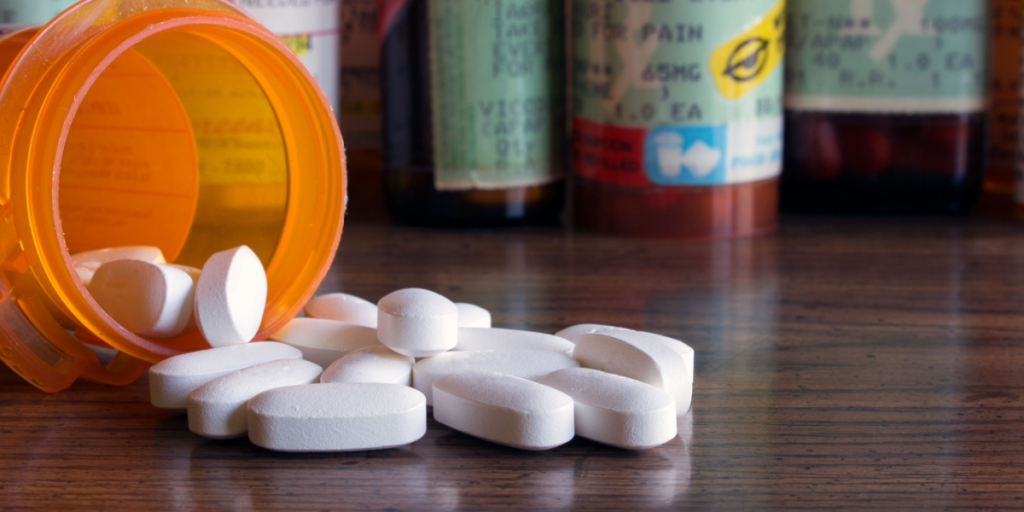

There is no specific treatment, but over-the-counter painkillers and rest can help manage symptoms.
Most people recover within two weeks, but joint pain can persist longer.
Also read
If you develop a sudden fever and joint pain after being in an outbreak area, seek medical advice immediately.


