Magnesium overdose can happen from taking too much from supplements, but not from foods.
Others are reading now
Magnesium is an essential mineral that supports a wide range of bodily functions, but too much can be harmful.
Here’s what you need to know about magnesium supplementation, safety, and potential risks.
This was reported by EatingWell.
Why Magnesium Is Important

Magnesium plays a critical role in the body, including:
- Protein synthesis
- Blood sugar and blood pressure regulation
- Energy production
- DNA and RNA synthesis
- Bone development
- Transporting calcium and potassium for muscle, heart, and nerve function
Because magnesium is involved in so many processes, maintaining adequate levels is essential for overall health.
Also read
How Overdose Can Happen
While magnesium obtained from food is generally safe, taking too much from supplements can cause problems.
The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for supplemental magnesium is 350 mg per day for adults.
Exceeding this limit, especially with high-dose products like magnesium oxide, citrate, or chloride, can lead to hypermagnesemia, or magnesium toxicity.
Common Symptoms of Excess Magnesium
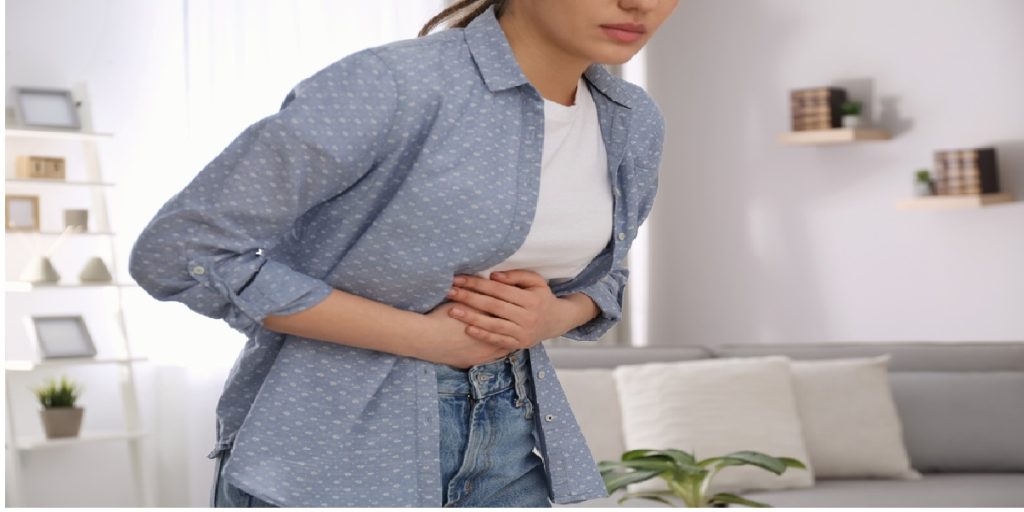

Early warning signs of magnesium overdose may include:
- Diarrhea and nausea
- Stomach cramps
- Vomiting
- Facial flushing
- Muscle weakness and lethargy
- Low blood pressure or irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- In severe cases, cardiac arrest
If you experience these symptoms, seek medical advice immediately, particularly if you have a kidney condition.
Also read
Recommended Dosage

The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium from all sources is:
- Ages 19–30: 400 mg (males), 310 mg (females)
- Ages 31+: 420 mg (males), 320 mg (females)
The UL of 350 mg applies only to supplements.
Magnesium obtained through foods like nuts, leafy greens, beans, dairy, and tofu does not pose a toxicity risk.
Who Should Be Careful

People with chronic illnesses or kidney dysfunction are at higher risk of magnesium overdose.
Extremely high doses, such as 5,000 mg in some antacids or laxatives, have been associated with toxicity.
Also read
Always follow label instructions and consult your doctor if unsure.
Medication Interactions
Magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications, including:
- Bisphosphonates (for osteoporosis), which may reduce magnesium absorption
- Certain antibiotics, which should be taken hours apart from magnesium supplements
- Diuretics, which can increase magnesium loss and cause deficiency
Choosing a Safe Supplement

If you need a magnesium supplement, experts recommend:
- Selecting high-quality, independently verified products
- Choosing forms with high bioavailability, like magnesium citrate
- Staying at or below the 350 mg supplemental limit unless advised otherwise
- Consulting a healthcare provider about potential interactions with other medications
Expert Advice

Magnesium is vital for your health, but too much can be harmful.
If you experience symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, irregular heartbeat, or muscle weakness after taking a supplement, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Also read
“It’s important to discuss your current diet and supplement use with your doctor to ensure safe and effective dosing,” says Dr. Laura Purdy, board-certified family physician.
By combining magnesium-rich foods with careful supplementation when necessary, you can safely reap the benefits of this essential mineral without risking toxicity.


