As the use of AI tools like ChatGPT surges, scientists are raising alarms about their hidden environmental cost. Behind every interaction lies a vast network of data centers with heavy energy and water demands — and consequences we’re only beginning to understand.
Others are reading now
As the use of AI tools like ChatGPT surges, scientists are raising alarms about their hidden environmental cost. Behind every interaction lies a vast network of data centers with heavy energy and water demands — and consequences we’re only beginning to understand.
AI’s rise: From novelty to necessity

AI usage has exploded in recent years, becoming a go-to resource for millions. With its growing capabilities, it’s now embedded in countless platforms — driving an arms race among tech giants to expand their AI infrastructure.
The power behind AI: Massive data centers
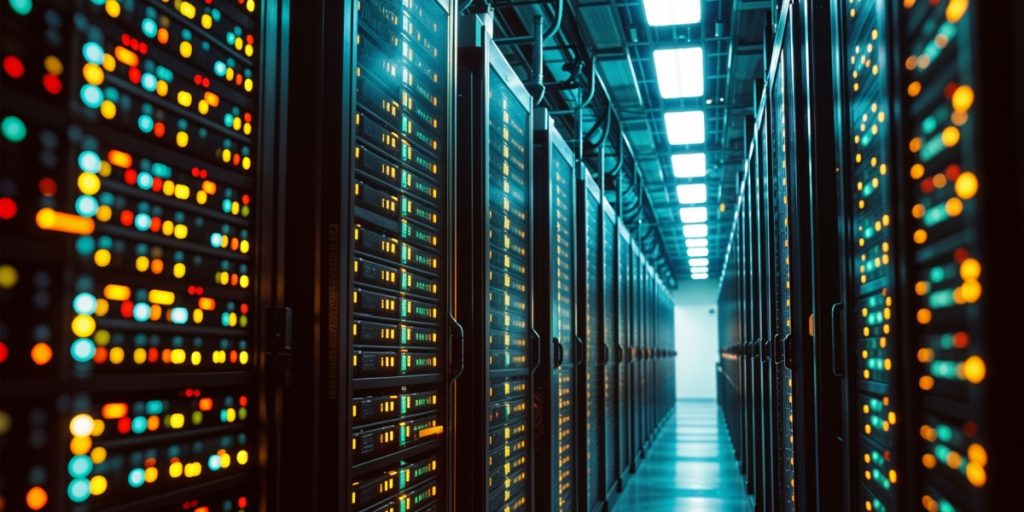

To meet this demand, companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google have built sprawling data centers. These facilities process enormous volumes of information — but at a significant environmental cost that remains largely overlooked.
ChatGPT uses 10x more energy than a Google search

According to Goldman Sachs, a single ChatGPT query consumes nearly ten times more energy than a traditional Google search. With global usage soaring, the cumulative energy impact is staggering — and growing.
Fossil fuels still power the grid

Most electrical grids still rely heavily on fossil fuels. As AI data centers draw more power, they contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, adding to the climate crisis while alternatives lag behind.
Also read
Local communities bear the burden

Residents near some data centers, such as those operated by Meta, report water contamination fears. Communities are increasingly vocal about the toll these massive facilities take on their land, water, and air.
AI is draining water supplies

A medium-sized data center can use about 300,000 gallons of water per day — roughly the same as 1,000 U.S. households. This water is primarily used to cool servers and is then lost as vapor, no longer usable for drinking or irrigation.
Water vapor and environmental loss
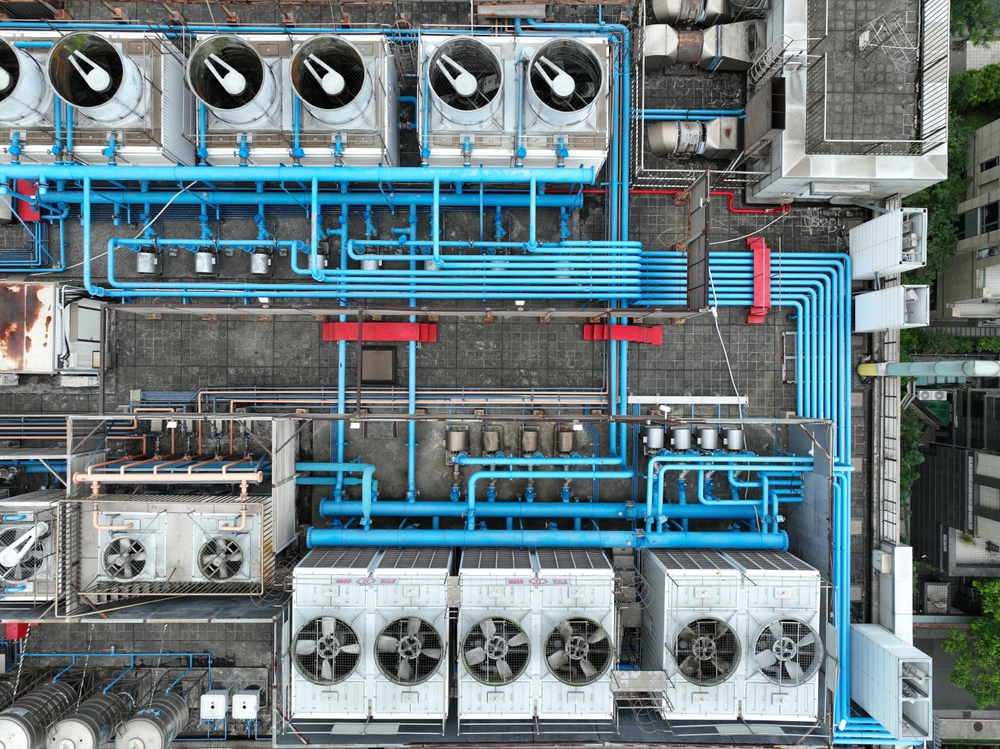
When used for cooling, water in data centers evaporates and is released into the atmosphere. Research from the University of California, Riverside, highlights that this process removes vital water resources from already stressed regions.
Industry secrecy fuels concern

Tech leaders like OpenAI CEO Sam Altman have largely avoided discussing their energy usage. Meanwhile, many companies quietly continue to rely on polluting energy sources while searching for cleaner alternatives.
Researchers speak out: “It’s a cause for concern”

Scientists are urging transparency and sustainability in the AI sector. With little regulatory oversight, the true cost of AI’s environmental footprint remains hidden — but its impact is already measurable.
Also read
A technology we can’t avoid — yet

AI is now embedded in nearly every service, making it difficult for users to opt out. This ubiquity means that even casual use contributes to environmental degradation, often without users knowing it.
The path forward: Balancing progress and responsibility

AI innovation continues to advance rapidly, but researchers stress the importance of sustainable practices. Striking a balance between technological progress and environmental stewardship is crucial — before the cost becomes irreversible.


